

When you access a database table through a Database Connection, query layer, or web service, ArcGIS filters out any unsupported data types.
DATA TYPES IN POSTGRESQL SERIAL
The UUID values guarantee a better uniqueness than SERIAL and can be used to hide sensitive data exposed to the public such as values of id in URL. The UUID data type allows you to store Universal Unique Identifiers defined by RFC 4122 . In addition, JSONB supports indexing, which can be an advantage. The JSON data type stores plain JSON data that requires reparsing for each processing, while JSONB data type stores JSON data in a binary format which is faster to process but slower to insert. PostgreSQL provides two JSON data types: JSON and JSONB for storing JSON data. The array comes in handy in some situations e.g., storing days of the week, months of the year. In PostgreSQL, you can store an array of strings, an array of integers, etc., in array columns. The TIMESTAMPTZ is the PostgreSQL’s extension to the SQL standard’s temporal data types. It is the abbreviation for timestamp with the time zone. TIMESTAMPTZ is a timezone-aware timestamp data type.


This is similar to AUTO_INCREMENT column in MySQL or AUTOINCREMENT column in SQLite. Serial is the same as integer except that PostgreSQL will automatically generate and populate values into the SERIAL column.Small integer ( SMALLINT) is 2-byte signed integer that has a range from -32,768 to 32,767.There are three kinds of integers in PostgreSQL: PostgreSQL provides two distinct types of numbers: Theoretically, text data is a character string with unlimited length. TEXT is the variable-length character string.PostgreSQL does not pad spaces when the stored string is shorter than the length of the column. With VARCHAR(n), you can store up to n characters. VARCHAR(n) is the variable-length character string.If you insert a string that is longer than the length of the column, PostgreSQL will issue an error. If you insert a string that is shorter than the length of the column, PostgreSQL pads spaces. CHAR(n) is the fixed-length character with space padded.PostgreSQL provides three character data types: CHAR(n), VARCHAR(n), and TEXT When you select data from a Boolean column, PostgreSQL converts the values back e.g., t to true, f to false and space to null. 0, no, false, f values are converted to false.1, yes, y, t, true values are converted to true.When you insert data into a Boolean column, PostgreSQL converts it to a Boolean value You use boolean or bool keyword to declare a column with the Boolean data type. Special types such as network address and geometric data.Ī Boolean data type can hold one of three possible values: true, false or null.Array for storing array strings, numbers, etc.UUID for storing Universally Unique Identifiers.
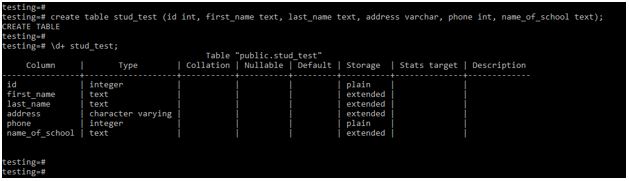
Temporal types such as date, time, timestamp, and interval.Numeric types such as integer and floating-point number.Character types such as char, varchar, and text.PostgreSQL supports the following data types: Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn about PostgreSQL data types including Boolean, character, numeric, temporal, array, json, uuid, and special types.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
